Determination of Mefenamic Acid in Pharmaceutical Drugs and Wastewater by RP-HPLC
Mohammad Anas Alfeen1*, Bashir Elias1, Youssef AlAhmad2
Affiliation
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Al-Baath University, Homs, Syria
2Department of Drug Control, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Baath University, Syria
Corresponding Author
Mohammad Anas Alfeen, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Al-Baath University, Homs, Syria; E-mail: mailto:chem_anas@yahoo.com
Citation
Alfeen, A.M., et al. Determination of Mefenamic Acid in Pharmaceutical Formulation and Wastewater by RPHPLC. (2017) J Anal Bioanal Sep Tech 2(2): 85- 88.
Copy rights
© 2017 Alfeen, A.M. This is an Open access article distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Keywords
Mefenamic acid (Ma); Tablets formulation; Wastewater; RP-HPLC
Abstract
This study presents a chromatographic analysis method for the determination of mefenamic acid in pharmaceutical preparations and treated wastewater from the pharmaceutical industry in East Asia and specifically (Syria). An isocratic RP-HPLC method has been developed for determination of Mefenamic acid on a Grace, alltima C18 column (250 x 4.6 mm, 5.0 μm) using a mobile phase consisting of (1%) Triethylamine aqueous buffer adjust pH = 2 by H3PO4 (85%): Methanol: Acetonitrile); (35: 20: 45 v\v\v %) at a flow rate of 2 mL/min. Detection was carried out at 220 nm. Retention time of Mefenamic acid was 7.85 ( ± 0.36) mins. The method was validated with respect to specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, ruggedness, and robustness.
The proposed method is simple, precise, sensitive, and reproducible and is applicable for quantification of Mefenamic acid in Tablets formulations and Wastewater developed and formulated in our laboratory.
Introduction
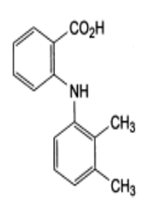
Mefenamic acid 2- [(2, 3-dimethylphenyl) amino] benzoic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with analgesic (Figure 1), anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties[1]. Mefenamic acid is official in IP[2], BP[3], USP[4] and EP[5]. Literature survey reveals the availability of several analytical methods being developed and validated for Mefenamic acid alone or in combination with other drugs. Various methods have been developed either for bulk or in oral dosage form[6-11]. But no analytical method has been reported for estimation of Mefenamic acid in topical formulation (Tablets) and Wastewater. The present study describes a validated isocratic RP-HPLC method for Mefenamic acid in a Tablet (topical formulation) and Wastewater developed and formulated in our laboratory.
Figure 1: Mefenamic Acid.
Experimental
Apparatus
RP-HPLC was performed on Lab Alliance machine Prominence LC pumps with a 20 μl sample injection loop and UV-Vis detector. The signal was recorded and integrated using Clarity Software.
Materials and Methods
Mefenamic Acid (MA); (purity 99.98%) was obtained as a gift sample from Merck Ltd, Germany. Methanol, Acetonitrile and Triethylamine was chemical solvents from Merck Ltd, Germany for Analytical HPLC grade. The Ultra-pure water for RP-HPLC was obtained by using the TKA Water Purification System, Germany. The Tablets formulation containing 500 mg/tab for MA was bought from the local market and Wastewater (Medico Labs-Homs-Syria\ Treatment wastewater Station in Pharmaceuticals Products).
Procedures
Chromatographic separation was carried out on a Grace, Alltima and 250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm C18 reverse phase column. Mobile phase consisting of (1%) Triethylamine aqueous buffer adjust pH = 2 by H3PO4 (85%): Methanol: Acetonitrile); (35: 20: 45 v/v %) was pumped at a flow rate of 2 mL/min. The elution was monitored at 220 nm and the injection volume was 20 μL. Validation of the method was performed following the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines[12].
Preparation of Standard and Sample Solution
(1%) Triethylamine aqueous buffer adjust pH = 2 by H3PO4 (85%): Methanol: Acetonitrile) used for the mobile phase were filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter (Ultipore N –66R Nylon 66; Pall Corp.,) and degassed by Ultra sonication for 15 min. The standard Stock solution was prepared by dissolving Mefenamic acid in Sodium Hydroxide Solution separately to get a solution containing 1mg /mL for Mefenamic acid. The working standard solution (1N) of Mefenamic acid was prepared by diluting 0.2 mL stock solution to 10 mL with Sodium Hydroxide Solution (1N) to obtain a solution containing 20 μg /mL Mefenamic acid.
10 Tablets were accurately weighed equivalent 10mg in 10 mL volumetric flask. About 0.5 mL of Sodium Hydroxide Solution (1N) was added, further was then vortexed and sonicated for 15 minutes. Volume was made up with Sodium Hydroxide Solution (1N) to obtain Sample Stock Solution of concentration 1000 μg/mL. This stock solution was filtered through 0.45 μm PTFE filter. The working sample solution was prepared by diluting 0.2 mL stock solution to 10mL with Sodium Hydroxide Solution (1N) to obtain a solution containing 20/μg mL Mefenamic acid. The drug present in the sample solutions was calculated by using the calibration curves. All the solutions were stored at (2 - 8)°C for future use.
Method Validation
Linearity
An eight-point (0.05, 0.1, 0.4, 1, 12, 22, 40 and 50) μg/ml calibration curves were prepared for the RP-HPLC method. The peak area for the RP-HPLC was obtained by injecting 20 μl of the drug solution into the column. Calibration curves were plotted by taking the peak area curve on the y-axis and the concentration (μg/ml) on the x-axis.
Precision and Accuracy
The intraday precision study was carried out to check the reproducibility of the results. A concentration of (2, 8, 20) μg/ml (n = 6) were analyzed to find out Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) for RP-HPLC methods. The recovery study was performed six times at each level. The amount of MA present in the sample was calculated using the calibration curves.
Robustness
The robustness of the RP-HPLC method was studied by deliberately changing the method parameters like flow rate of the mobile phase, detection wavelength, and organic phase composition. A series of system suitability parameters like retention time, theoretical plates, and tailing factor were determined for each changed condition according to ICH[12].
Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantization
The LOD and LOQ were determined separately according to the ICH guidelines[12]. For the RP-HPLC method, concentrations providing a signal-to-noise ratio 3:1 and 10:1 were considered as the LOD and LOQ, respectively.
Results and Discussion
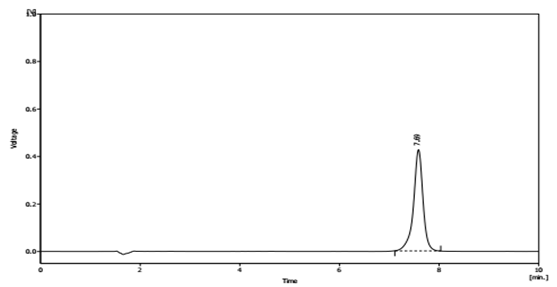
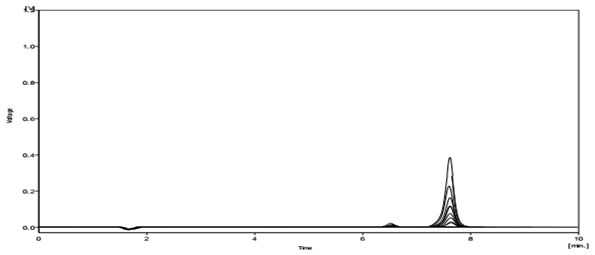
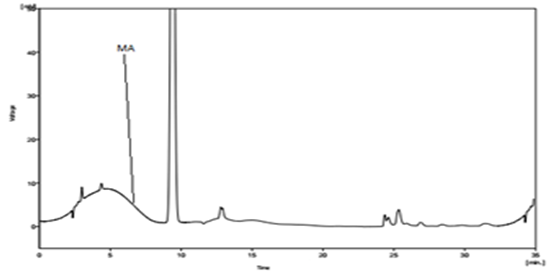
Several mobile phase compositions were tried. A satisfactory separation and good peak symmetry were obtained by using the described (1%) Triethylamine aqueous buffer adjust pH = 2 by H3PO4 (85%): Methanol: Acetonitrile) (35: 20: 45 v/v %). Quantification was achieved with UV detection at 220 nm. Representative chromatograms of standard Mefenamic acid and Mefenamic acid in Tablet (topical formulation) and Wastewater are shown in (Figure. 2) and (Figure. 3) respectively.
Figure 2: Chromatogram of Mefenamic Acid in Tablet Topical Formulation (R.T. 7.69 (±1.10)) at 220 nm.
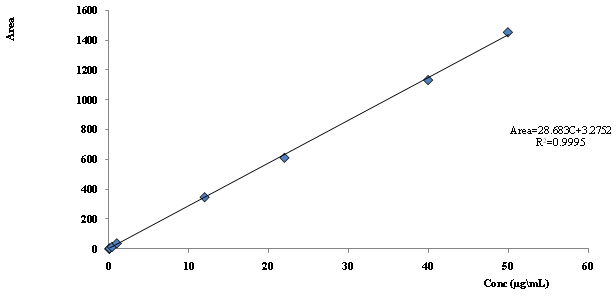
System suitability tests were carried out on freshly prepared standard solutions (n = 6) containing Mefenamic acid. System suitability parameters obtained with 20 μL injection volumes are summarized in (Table 1). Linearity regression data are summarized in (Table 2), which shows a good linear relationship between concentration of Mefenamic acid and peak areas was obtained over a concentration range of 0.05 – 50 μg/mL (Figure. 4).
Figure 3 Calibration Curve Diagram for Mefenamic Acid.
Table 1: System Suitability Test Parameters for Mefenamic Acid.
| Parameter | Mefenamic Acid (MA) |
| Slope | 28.683 |
| Intercept | 3.2752 |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.9995 |
| Detection Wavelength, nm | 220 |
| Linear rang, μg/mL | 0.05-50 |
Table 2 Analysis of method parameters and regression data.
| Name Compound | Area (mV. s)n = 6) | Number of Theoretical Plate (n = 6) | Tailing Factor (n = 6) |
| Mefenamic Acid (MA) | 789.759 | 8462 | 0.983 |
Figure 4: Calibration Curve Diagram for Mefenamic Acid (0.05 - 50) μg/ml.
The correlation coefficient (r2) was found to be 0.9995 for Mefenamic acid which ensures that a good correlation existed between the peak area and analyte concentration. The LOD was found to be 0.04 μg/mL for Mefenamic acid. LOQ was found to be 0.06 μg/mL these values indicate that the method is sensitive. In the precision studies, RSD of mean assay values was found to be 1.49% for Mefenamic acid. These % RSD values which are well below 2% indicate that the repeatability of this method is satisfactory. Thus, there exists a closeness of agreement in repeated measurements of peak response.
Accuracy studies indicated that the percent recoveries were obtained from the difference between the areas of spiked and unsliced samples. The mean recovery of the added standard drug was 99.78%. This means recovery value is well within the range of 98 - 100%, indicating the method is accurate. Specificity studies indicated good resolution was obtained between the drugs and excipients showing complete separation of mefenamic acid. No interference from excipients, impurities, or degradation products ensured that the peak response was due to mefenamic acid only. Indicating that method is robust i.e. it is reliable during normal use. All the validation data are summarized in (Table 3).
Table 3: Summary of validation parameters.
| Parameter | Recovery% | RSD% | LOD μg/ml | LOQ μg/ml | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mefenamic Acid | 99.78 | 1.49 | 0.04 | 0.06 | ||||
The assay results obtained by using the proposed method for the analysis of developed Tablet formulation containing Mefenamic Acid. Acid in different Wastewater (n = 3) Indicating that method is robust i.e. it is reliable during normal use. All the validation data are summarized in (Table 5). The Chromatogram of extract from Wastewater after SPE Procedure (Figure. 5). The assay results obtained by using the proposed method for the analysis of developed Wastewater in Pharmaceuticals Productions Company.
Table 4 Parameters of Calibration curvers, linearity ranges, and LOD and LOQ Values.
| Drug | Linear range (μg/mL) | Slope | Intercept | R2 | LOD (μg/L) | LOQ (μg/L) |
| Mefenamic Acid (MA) | 0.5-10 | 50.74 | -13.311 | 0.9995 | 0.183 | 0.548 |
| 0.09-10 | 191.483 | 5.801 | 0.9999 | 0.029 | 0.086 | |
| 0.32-10 | 392.615 | -128.711 | 0.9998 | 0.105 | 0.315 | |
| 0.300-10 | 233.389 | 1.237 | 0.9999 | 0.010 | 0.030 |
Figure 5: The Chromatogram of extract from Wastewater after SPE Procedure.
Table 5: Concentrations and standard deviations (μg/L) of Mefenamic Acid in different surface water (n = 3).
| Name Wastewater | Mefenamic Acid (MA) |
| Near Medico Labs | 0.022 |
| In Medico Labs | < LOQ |
| Behind Medico Labs | 0.015 |
| In Front of Medico Labs | 0.021 |
| Medico Labs Station | 0.012 |
The correlation coefficient (r2) was found to be 0.9995 to 0.9999 for Mefenamic acid which ensures that a good correlation existed between the peak area and analyte concentration in Wastewater. The LOD was found to be 0.02 to 0.183 μg/L for Mefenamic acid. LOQ was found to be 0.08 to 0.548 μg/L (Table 4). Concentrations and standard deviations (μg/L) of Mefenamic.
Conclusion
The proposed RP-HPLC method is accurate, precise, sensitive, selective, and rapid for the determination of Mefenamic acid in a Tablet (topical formulation) and Wastewater developed and formulated in our laboratory.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to Medico Labs Pharmaceutical Company, Homs, Syria for providing the gift sample of Mefenamic Acid and Wastewater in Treatment Station.
References
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[2] Indian Pharmacopoeia 6th Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission. (2010) 2: 1641-1642.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[3] British Pharmacopoeia. (2005) 2: 1267-1268.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[4] U.S. Pharmacopoeia 30. (2005) 2: 2560.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[5] European Pharmacopoeia 6th edition. (2008) 2: 2349-2350.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[6] Premanand, D.C., Senthilkumar, K.L., Saravanakumar, M., et al. New RP-HPLC Method Development and Validation of Mefenamic Acid and Drotaverine Hydrochloride in Combined Dosage Form. (2011) J Pharm 1: 07-11.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[7] Prajapati, D., Hasumati, R. Simultaneous Estimation of Mefenamic Acid and Dicyclomine Hydrochloride by RP-HPLC Method. (2012) Int J Pharm bio sci 3(3): 611-625.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[8] Singh, H., Kumar, R., Singh, P. Development of UV Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Mefenamic Acid in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. (2011) Int J Pharm Pharmaceu Sci 3(2): 237-238.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[9] Padmalatha, H., Dr. Vidyasagar, G. Validated RP - HPLC Method for the Estimation of Mefenamic acid in Formulation. (2011) Int J Res Pharmaceu Biomed Sci.2: 1261-1265.
Pubmed || Crossref || Others
[10] Sultana, N., Arayneb, M., Naveed, S. Simultaneous Quantitation of Captopril and NSAID’s in API, Dosage Formulations and Human, Serum by RP-HPLC. (2010) J Chin Chem Socie 57(1): 62-67.
[11] Muhammad, N. Simultaneous Determination of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Human Serum by Reversed Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography. (2012) Quim Nova 2: 939-943.
[12] International Conference on Harmonization Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1) Geneva Switzerland. (1996).
Pubmed || Crossref || Others